SCM refers to a collection of tools used by DevOps, optimizing the process of software development, tracking changes made to a source code repository, integrating with other tools, and facilitating code maintenance.
Under an SCM strategy, the team of developers works in a project, that is, a repository for source code and a place for planning, tracking progress, and collaborates on building the software. Ordinarily an SCM has also communication tools like wiki and issue tracking, so the team of developers can interact and work together in the same environment, documenting, fixing, and following bugs and issues. Under the Scrum strategy, widely used these days, it's common working with Kanban and metrics tools.
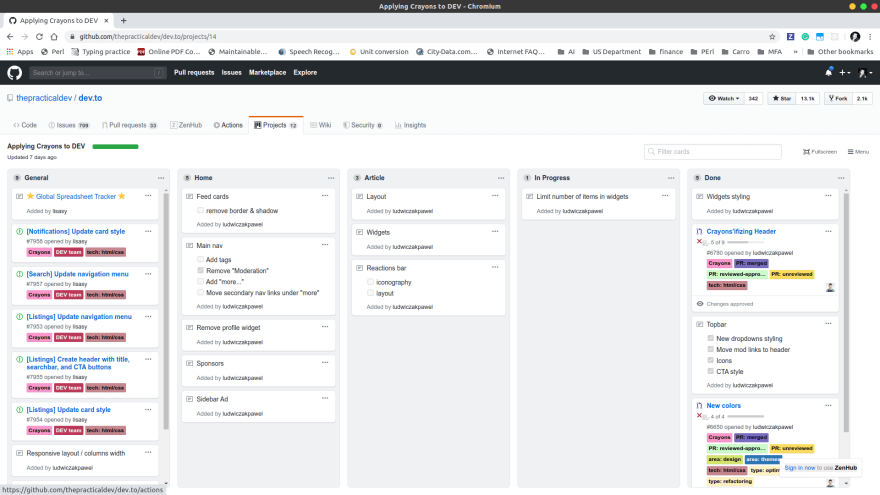
The repository in the project is the container where data is stored and should be organized in branches, tags, and releases.
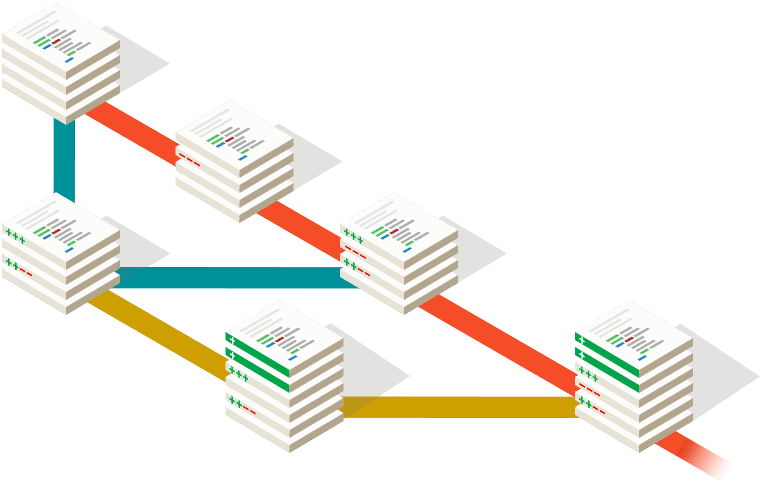
It’s a current practice to work with teams dealing with the same pieces of code concurrently. As each individual has its own ways of working, eventually the project under development could become broken or unmanageable in some circumstances. SCM may solve this problem by committing, merging, and rewinding changes to the source code repository, so the code should be placed into normal production while ensuring high-quality code by handling continuous integration and testing.

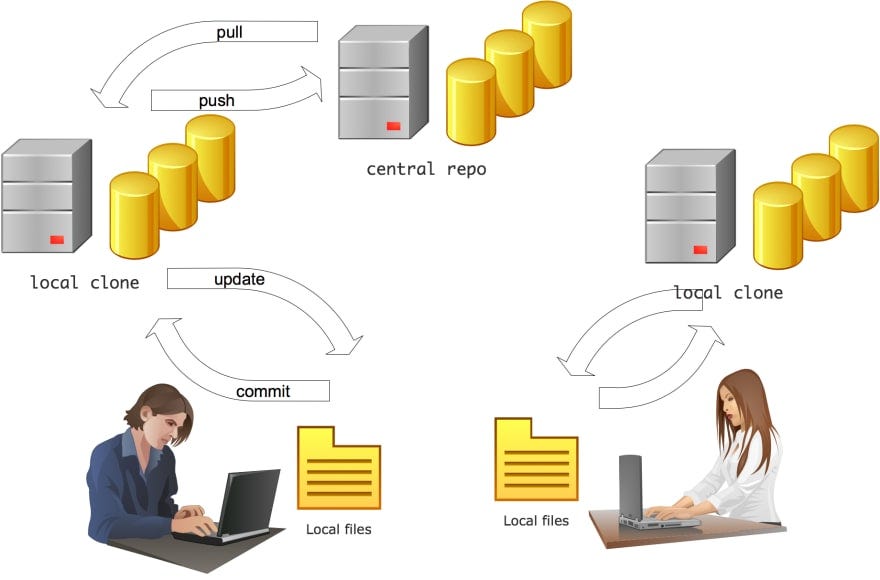
The horsepower of SCM is the named VCS or Version Control System. It deals with the concurrency of versions and maintains copies of all code made, classifying it by date, user, and branch. We say a chunk of code is committed to a VCS when the modified file is added to the stack of changes. When the VCS is not centralized, using the client-server paradigm, we name it DVCS or Distributed Version Control System.

Other components of this toolchain include Configuration Management, Continuous Integration, and Continuous Delivery.
We strongly recommend using Git as DVCS. It’s one of the most used version control these days, having lots of functionalities, integrations with other tools you will need. It is in the most used web apps implementing DevOps tools, like GitLab and GitHub. Go there and create your account. Begin your DevOps adventure!